Industry Without a Footprint: Challenges and Opportunities of Industrial Decarbonization
As we have seen in previous blog posts, decarbonization, understood as the progressive reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, is a crucial global challenge in mitigating the effects of climate change. In the industrial sector, this process represents a significant transformation, marked by technical, economic, and regulatory challenges, but also by the emergence of innovative opportunities that can redefine the future of businesses. Below, we explore the main challenges and opportunities associated with industrial decarbonization.
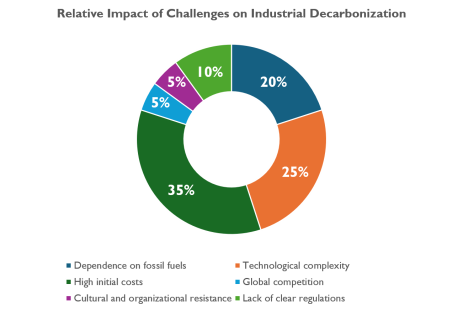
Obstacles on the Path to Net Zero: What Challenges Does the Industry Face?
As industries move towards decarbonization, they encounter complex challenges such as:
High Initial Costs
Implementing low- or zero-carbon technologies requires significant investments. This includes adopting renewable energy sources, installing carbon capture and storage (CCUS) systems, or modifying technologies (such as combustion versus electrification). These investments can be prohibitive for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which often have limited financial resources.
Technological Complexity
The transition to more sustainable industrial processes involves adopting advanced technologies that are not always readily available or sufficiently developed. Sectors such as cement, steel, and chemicals face particular challenges due to the high energy intensity of their processes and the difficulty of finding viable short-term alternatives.
Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Many industrial sectors are deeply reliant on fossil fuels as both an energy source and a raw material. Replacing this dependency requires not only a technological shift but also a structural change in supply chains.
Lack of Clear and Uniform Regulations
While governments have begun implementing policies to encourage decarbonization, many regions lack coherent and standardized regulations. This creates uncertainty for companies, making long-term planning more difficult.
Cultural and Organizational Resistance
The shift towards a more sustainable model can encounter resistance within organizations due to lack of knowledge, risk aversion, or concerns about potential productivity impacts. This cultural obstacle can delay the adoption of decarbonization initiatives.
Global Competition
Industries in countries with strict climate regulations face competitive challenges compared to those in regions with more lenient environmental policies. This can lead to “carbon leakage,” where companies relocate operations to countries with fewer environmental restrictions.
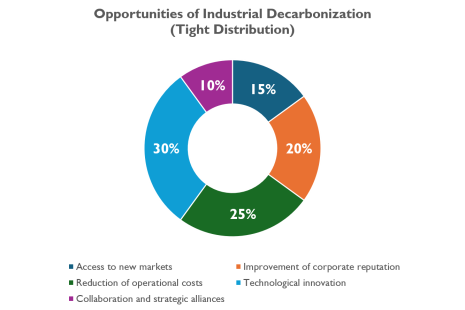
Decarbonization as a Driver of Change: New Opportunities for Industry
Despite these challenges, decarbonization is driving industrial transformation and unlocking new opportunities, such as:
Technological Innovation
The need to reduce emissions has fueled the development of new technologies, including:
- Green hydrogen, positioned as a key alternative fuel for industrial sectors that are difficult to electrify.
- Process electrification, where adopting renewable energy sources to electrify equipment and operations increases efficiency and reduces emissions.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCUS), which, although still in development, has the potential to revolutionize emissions management in industries.
These innovations not only improve sustainability but can also create competitive advantages for companies leading their implementation.
Reduction of Operating Costs
Although initial costs can be high, sustainable technologies tend to generate long-term savings. For example, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can significantly reduce energy expenses compared to fossil fuels.
Enhanced Corporate Reputation
The transition to sustainable practices strengthens a company’s reputation among consumers, investors, and key stakeholders. In a market where consumers are increasingly aware of environmental impact, sustainable companies are more likely to gain loyalty and market share.
Access to New Markets
Decarbonization opens the door to emerging markets focused on clean technologies, such as battery production, sustainable materials, and renewable energy equipment. Additionally, international agreements and regulations, such as the European Green Deal, are driving the creation of global markets for low-carbon products.
Collaboration and Strategic Partnerships
The complexity of the decarbonization process has led to the formation of public-private partnerships, collaborations between companies, and cooperation with academic institutions. These synergies accelerate the development of solutions and create mutual benefits.
From Challenges to Action: Strategies to Overcome Barriers and Seize Opportunities
On the path to a carbon-free industry, challenges are numerous, but opportunities are even greater. To navigate this transformation successfully, companies should consider:
Setting Clear and Measurable Goals
Businesses must define decarbonization objectives aligned with global sustainability goals. This provides a clear roadmap to guide actions and measure progress.
Innovating Through Digitalization
Digitalization can optimize industrial processes, improve energy efficiency, and reduce emissions. Tools such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics are essential for monitoring and controlling environmental performance.
Investing in Research and Development (R&D)
Supporting research and development (R&D) is crucial for creating disruptive technologies that enable a faster and more effective transition to sustainability.
Implementing Circular Economy Models
The circular economy provides solutions to reduce resource consumption and minimize waste through recycling, reuse, and process optimization.
Strengthening Training and Awareness
Companies should invest in employee training to ensure that all levels of the organization understand the importance of decarbonization and actively participate in its implementation.
Promoting Multisector Collaboration
Bringing together efforts from different industrial sectors, governments, and communities is essential to address the complex challenges of decarbonization.
Revolutionizing Industry: The Transformative Power of Businesses in Industrial Decarbonization
Industrial decarbonization is not just an ethical obligation in response to the climate crisis but a strategy that redefines the future of global industry. Companies have the opportunity to lead this transformation, demonstrating that a business model can be both profitable and sustainable.
Clear examples include:
- ArcelorMittal, a leader in the steel sector, implementing innovative hydrogen-based technology to replace coal in low-emission steel production.
- IKEA, the Swedish company committed to becoming carbon positive by 2030, investing in renewable energy and sustainable materials.
- Tesla, the American company that, although focused on mobility, is driving electrification and sustainability in the industrial supply chain.
The journey towards an industry without a carbon footprint is not without challenges. However, the message is clear: industrial decarbonization is not only a duty to future generations but also an opportunity to reinvent entire sectors, strengthen business resilience, and ensure competitiveness in a world demanding sustainability. Companies that take action today will be better positioned to thrive in the future.
Don’t miss the next blog on decarbonization: “The Strategic Role of Water in Industrial Decarbonization: Challenges and Opportunities.”
References
- The European Green Deal, European Commission: European Green Deal
- Industrial Decarbonization: Challenges and Opportunities, FUNCAS: FUNCAS Report